Key To Markets Review: Unregulated Broker Risk Alert
Is Key To Markets safe? Revoked regulation, user complaints, and withdrawal issues raise red flags. Read this WikiFX review before you deposit.
简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
Abstract:We've covered what is buy limit in forex, how it compares to other orders, the practical steps to place one, and advanced strategies for its application. We've also been honest about its inherent risks. Your next step is to open a demo account and practice. Set up trades using support levels, trendlines, and Fibonacci retracements. Get a feel for the process, experience an order being missed, and see a plan come together perfectly. This practice is what builds the confidence and skill to use what is buy limit in forex as a cornerstone of your live trading, fostering the precision, discipline, and planning that define a successful trader.
A buy limit in forex is a pending order that tells your broker to buy a currency pair at a specific price that is *below* the current market price, or at a better price. Think of it like shopping online for something you want, but you don't want to pay today's price. Instead of checking back every day, you set an alert that automatically buys the item for you the moment it hits your target sale price. That's basically how a buy limit order works.
This simple tool is a key part of smart, planned trading. It lets us enter the market at a price we chose ahead of time based on our research, all without staring at the screen waiting for the perfect moment. It changes trading from a quick, emotional activity into a planned, organized approach. This guide will go far beyond just explaining what it means. We will look at the main strategies, the practical steps, and the important risk factors that separate professional traders from beginners. We will show you exactly *how* and *why* to use the buy limit order to improve your trading accuracy and discipline.
Why would a trader choose to wait for a lower price instead of simply buying at the current market rate? The answer comes down to strategy, risk management, and discipline. Using a buy limit order is a deliberate choice to trade on your own terms, not the market's. The main benefits are:
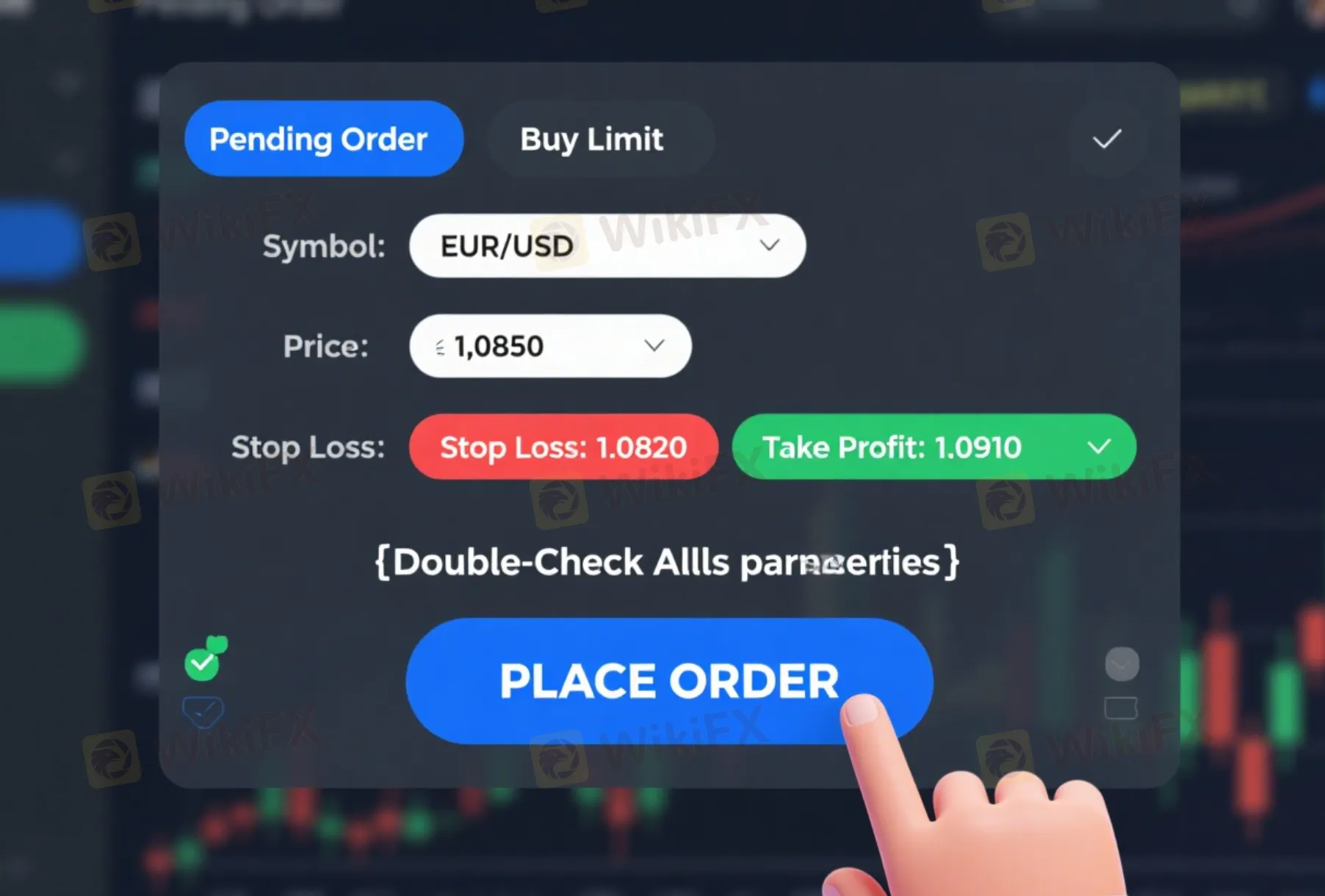
The main goal of a buy limit order is to follow the old trading wisdom: “buy low, sell high.” By setting an order below the current price, we are planning to enter a long position at a price that is better than what is available right now. For example, imagine the EUR/USD is currently trading at 1.0900, but our analysis shows a strong support level at 1.0850. We believe the price will drop to test this support before rising. Instead of buying at 1.0900, we place a buy limit order at 1.0850. If our analysis is correct, the market will execute our trade at this better price, increasing our potential profit from the following rise.
Emotion is one of the biggest enemies a trader faces. The fear of missing out (FOMO) can cause us to chase a rising price, while fear of loss can make us hesitate at the best entry point. A buy limit order acts as protection against these emotional impulses. The analytical work is done beforehand—in a calm, objective state. We identify our level, set the order, and define our risk. Once the order is placed, our plan runs automatically. The market will either come to our price, triggering a trade based on our plan, or it won't. This mechanical execution builds discipline and prevents the costly mistakes that come from making quick decisions.
Buy limit orders are not placed at random prices. They are a tool for executing a specific trade idea at a specific location on the chart. These locations are key technical levels where the chance of a price reaction is higher. These are areas we identify through careful analysis, such as historical support zones, dynamic trendlines, or key Fibonacci retracement levels. By placing a buy limit at these points of confluence, we are not just guessing; we are strategically positioning ourselves to enter the market where buying pressure is expected to emerge, providing a higher chance of a successful trade.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week. No trader can monitor every chart, every currency pair, all the time. Pending orders, including buy limits, are essential tools for effective time management. We can perform our analysis on multiple currency pairs, identify potential setups, and set our buy limit orders across our entire portfolio. This allows the market to come to us. We can step away from the charts, knowing that our trading plan is in place and will be executed automatically if our conditions are met. This frees up mental energy and time, preventing burnout and allowing for a more balanced approach to trading.

To truly master the buy limit, we must understand how it differs from other essential order types. This knowledge is not optional for any serious trader; it is the foundation of precise trade execution. The most common confusion happens between a buy limit and a buy stop, but it's also important to distinguish it from a simple market order.
A market order is about speed. You are telling your broker, “Buy this for me right now, at the best available price.” It's for situations where speed is more important than the exact entry price. A buy limit, in contrast, is about patience and price. You are saying, “Buy this for me only if the price drops to this specific level or lower.”
This is the most important distinction to understand. Both are pending orders to buy a currency pair, but they are based on opposite expectations of future price movement relative to the current price.
A buy limit is set *below* the current market price. The trader's expectation is that the price will drop down to their entry level (the limit price) and then reverse to the upside. This is a “buy on a dip” or “buy on a pullback” strategy.
A buy stop is set *above* the current market price. The trader's expectation is that if the price rises to their entry level (the stop price), it will trigger a breakout and continue to move higher. This is a “buy on a breakout” or “momentum” strategy.
In short:
To provide complete clarity, we can organize all the primary order types into a single matrix. This table serves as a permanent reference guide for choosing the right order for any trading scenario.
| Order Type | What It Does | Price Level vs. Current Price | Trader's Expectation | Analogy |
| *Buy Limit* | Buys an asset at a specific price *or lower*. | *Below* current price | The price will *fall* to the entry level, then *rise*. | “I'll buy it if it goes on sale.” |
| *Buy Stop* | Buys an asset when the price *rises* to a certain level. | *Above* current price | The price will *break out* and continue to *rise*. | “If it hits that high, it's going higher.” |
| *Sell Limit* | Sells an asset at a specific price *or higher*. | *Above* current price | The price will *rise* to the entry level, then *fall*. | “I'll sell it if the price gets this good.” |
| *Sell Stop* | Sells an asset when the price *falls* to a certain level. | *Below* current price | The price will *break down* and continue to *fall*. | “If it drops that low, it's going lower.” |
Understanding this matrix is fundamental. Each order type is a specific tool designed for a specific job. Using a buy limit when a buy stop is required (or vice versa) will lead to failed strategies and significant losses.
Moving from theory to practice is where a trader's skill is built. Placing a buy limit order is a straightforward process on most trading platforms like MetaTrader 4/5 or cTrader. However, the mechanical steps are only part of the story. The real expertise lies in the thought process behind each parameter we set. Let's walk through the complete process, from analysis to execution.
This is the most important step, and it happens entirely before we even think about opening an order ticket. The price we choose for our buy limit is not a guess; it is the product of analysis.
Here is our thought process: We are looking at the GBP/JPY 4-hour chart. The pair is in a clear uptrend, but has recently pulled back from its highs. We've analyzed the chart and identified a strong horizontal support level at 199.50, an area where price has bounced multiple times in the past. Our trade idea is that the price will continue its short-term drop to retest this powerful support zone before resuming its primary uptrend. Therefore, 199.50 becomes our desired entry price. We are not interested in buying at the current price of 200.10; we want the discount that a retest of support provides.

With our entry price identified, we now move to our trading platform. We navigate to the chart of the asset we want to trade (GBP/JPY in our example) and open the “New Order” window. By default, the platform will likely be set to “Market Execution” or “Instant Execution.” We need to click on this field and change the order type. From the dropdown menu, we first select “Pending Order.” This will reveal another set of options, from which we will specifically choose “Buy Limit.”
Now we input the details of our pre-planned trade. This is where we translate our analysis into concrete instructions for our broker.
After double-checking all the parameters—Symbol, Price, Stop Loss, Take Profit—we click the “Place” button. The order is now live. It will appear in the “Trade” or “Terminal” window of our platform, listed as a pending order. On the chart itself, we will see horizontal lines representing our entry price, stop loss, and take profit levels.
The work is now done. We have analyzed, planned, and executed. The order is in the hands of the market. This process reinforces discipline, allowing us to manage our trades based on a plan rather than reacting to every small price fluctuation.
Once we are comfortable with the mechanics of placing a buy limit order, we can elevate its use from a simple function to a sophisticated strategic tool. Advanced traders use buy limits with precision in specific, high-probability scenarios. Here are three professional strategies you can begin to incorporate into your trading.
This is the most classic and reliable strategy for a buy limit order. It's based on the principle that a price level that has previously acted as a floor (support) is likely to do so again.
The concept is to identify a clear, well-defined horizontal support zone on a chart. This is a price area where the market has reversed from a downtrend to an uptrend multiple times in the past. The more “touches” a support level has, the more significant it is considered. A key piece of expert knowledge is that support levels identified on higher timeframes, such as the Daily or Weekly charts, carry far more weight than those found on a 15-minute chart.
Execution:
1. Scan higher timeframe charts (e.g., H4, Daily) for clear horizontal support levels.
2. Wait for the price to approach this level from above.
3. Place a buy limit order slightly *above* the precise support line. For instance, if support is at 1.2500, we might set our order at 1.2505. This increases the chance of our order being filled, as the price may reverse just before touching the exact line.
4. Set a stop loss a reasonable distance below the support zone to protect against a breakout to the downside.
In a healthy, established uptrend, the price does not move in a straight line. It moves in a series of “impulses” (higher highs) and “corrections” or “pullbacks” (higher lows). This strategy uses a buy limit order to enter the market during a temporary pullback, positioning us to profit from the next impulse wave higher.
The concept is to identify a clear uptrend structure and use a dynamic level of support—like a rising trendline or a previous swing low—as our entry point.
Execution:
1. Identify a currency pair making a consistent series of higher highs and higher lows.
2. Draw a trendline connecting the higher lows. This line now acts as dynamic support.
3. As price pulls back towards the trendline, place a buy limit order at or slightly above the trendline.
4. Alternatively, identify the last significant “higher low” (a previous swing point) and place the buy limit order at that level, anticipating a retest.
5. The stop loss should be placed below the trendline or the swing low structure to invalidate the trade if the uptrend structure breaks.
This is a more advanced technique that uses the Fibonacci sequence to identify potential support levels during a pullback. It provides a mathematical and objective way to find high-probability entry points.
The concept is that after a significant upward price move (a swing), the price will often retrace a predictable portion of that move before continuing in the original direction. The Fibonacci retracement tool highlights key percentage levels for these potential reversals.
Execution:
1. Identify a clear and recent swing in an uptrend, from a significant swing low to a significant swing high.
2. Select the Fibonacci retracement tool on your platform and draw it from the bottom of the swing (the swing low) to the top of the swing (the swing high).
3. The tool will project several horizontal lines on your chart at key Fibonacci ratios: 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%. These are your potential “buy the dip” zones.
4. The 50% and 61.8% levels are often considered the most significant retracement zones for placing buy limit orders. We can place a buy limit order at one of these levels, anticipating a bounce.
5. For a higher-probability setup, look for a confluence where a Fibonacci level aligns with another technical element, such as a horizontal support level or a rising trendline. This alignment significantly strengthens the entry signal.
6. Place the stop loss below the next Fibonacci level or below the entire swing low.
No trading tool or strategy is perfect. A core part of professional trading is understanding the potential downsides and knowing how to reduce them. Being honest about the risks of buy limit orders is essential for long-term success and builds trust in our methods. Here are the primary limitations to be aware of.
The buy limit order, when fully understood, is far more than a simple platform function. It is a strategic instrument for implementing a well-defined trading plan with precision and discipline. It transforms a trader's mindset from reactive to proactive, shifting the focus from chasing the market to letting well-analyzed opportunities come to you. By mastering its use, we gain the ability to enter at more favorable prices, to remove destructive emotions from our execution, and to efficiently manage our time and a diverse portfolio.
We've covered what is buy limit in forex, how it compares to other orders, the practical steps to place one, and advanced strategies for its application. We've also been honest about its inherent risks. Your next step is to open a demo account and practice. Set up trades using support levels, trendlines, and Fibonacci retracements. Get a feel for the process, experience an order being missed, and see a plan come together perfectly. This practice is what builds the confidence and skill to use what is buy limit in forex as a cornerstone of your live trading, fostering the precision, discipline, and planning that define a successful trader.
Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
Is Key To Markets safe? Revoked regulation, user complaints, and withdrawal issues raise red flags. Read this WikiFX review before you deposit.

Is VORBIX MARKETS safe? Read this WikiFX review on no license status, withdrawal issues, and trader complaints before you deposit. Download now.

CySEC has told Cyprus brokers to prepare for on-site inspections and desk reviews focused on conflicts of interest and retail product sales.
Read this amana review covering broker regulation, user complaints, and withdrawal risk signals on WikiFX before you deposit. Check the facts now.
